Melissa Data Quality Platforms
Melissa's Full Spectrum DQ Approach. Learn MoreMelissa Data Quality Tools
Verify, correct & cleanse contact data in 240+ countries.Melissa Identity Verification
Increase compliance, reduce fraud and improve onboarding. Visit Identity Verification SolutionsMelissa E-Commerce / CRM
Improve customer onboarding, marketing & fulfillment.Melissa Enrich
Gain insight into who and where your customers are.Melissa Industries
See how Melissa's solutions work across industries.Data Hygiene
Keep your mailing list up-to-date, qualify for postal discounts & reduce UAA mail.Data Enhancement
Enrich your consumer or business records for greater insight & omni-channel marketing success.SaaS
Clean and update your data in the cloud, no software to maintain.Verify & enrich your records with multi-sourced, authoritative reference datasets.
Email Verification
Validate, standardize & score the deliverability of international emails in real time.
Melissa Global Email Verification can remove up to 99% of bad email addresses to increase deliverability, avoid high bounce rates and blacklisting, and protect your valuable sender reputation.
- Ping each email in real time to ensure it is active and can receive mail to ensure a successful campaign
- Improve deliverability by correcting typos, misspelled domains, and illegal characters that lead to high bounce rates.
- Reduce fraud by confirming only valid enter your systems
- Maintain CAN-SPAM compliance with FCC mobile domain detection
What We Do
The Simple Solution to Check & Verify Email Addresses to Improve Email Deliverability
Email Verification Features Provides:
- Deliverability Confidence Score: Measure deliverability with precision. Our score scales from 0-100, offering a dynamic score to simplify marketing decisions and protect your sender reputation.
- Predictive Accept-All Validation: Go beyond basic detection of accept-all addresses. Our predictive validation determines deliverability potential, minimising risks in sending when leveraging the Deliverability Confidence Score.
- Clear and Actionable Result Codes: Quickly understand and categorise email types with our intuitive result codes—no guesswork required.
- Syntax and Domain Correction: Global Email corrects syntax first, ensuring each email address is validated accurately. Robust syntax rules and domain correction algorithms can correct common typos and improve the user experience.

Melissa G2 Awards
Always recognized and praised





How It Works
How Our Email Verification Solution Works

Input
Validates an address at point of entry so bad data never enters your system.

Parse & Standardise
Identifies common syntax errors, illegal characters and parses individual email address components. Checks and corrects most misspelled domain names, standardises casing.

Privacy Flag
The Privacy Flag will show a “Y” if the Top Level Domain might adhere to privacy laws such as GDPR.

Email Mailbox Verify
SMTP ping in real time to determine address exists and can receive email.

Deliverability Confidence Score
Returns the percentage probability that an email will successfully reach the intended mailbox.

Output
A clean, deliverable address ready for mailing, order fulfilment, or analytics.
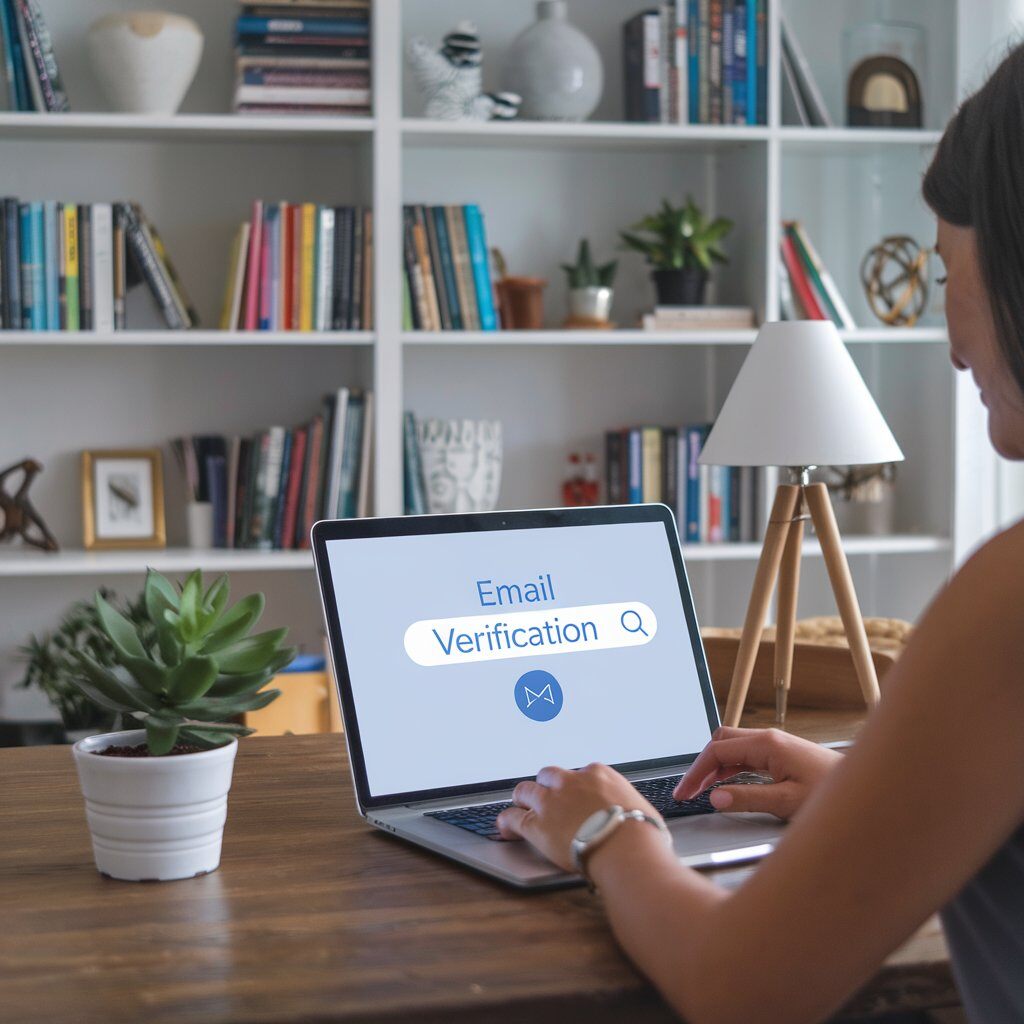
Deliverability Confidence Score (DCS)
Our Deliverability Confidence Score (DCS) combines a range of variables and email validation methods to predict the likelihood that a message will successfully reach its intended inbox. The DCS consolidates the validation results and simplifies it to a score from 0 to 100. This score helps you focus on emails that are not only valid but also more likely to be active and engageable. Leveraging DCS to refine your email marketing lists will ensure you reduce bounces and increase ROI.
Determining Factors for DCS:
- Validation Status - The overall status as well as any special flags associated with an email.
- Email Metadata - Information such as email age and historical engagement provides valuable insights into the email’s activity level.
- Domain Information - The type and security architecture of a domain help predict any complications with email delivery.
Predictive Accept-All Validation
Our Predictive Accept-All Validation feature offers a unique approach to evaluating emails hosted on accept-all servers. While these servers might typically mask inactive or invalid addresses, our proprietary Predictive Accept All algorithm analyses patterns and traces of historical activity, giving users a reliable window into the likelihood of successful delivery.
- Accept all domains are configured to accept emails sent to any address, regardless of whether that specific address actually exists or is inactive.
- The predicted deliverability of an accept all mailbox will be reflected by the Deliverability Confidence Score (DCS) for that email.

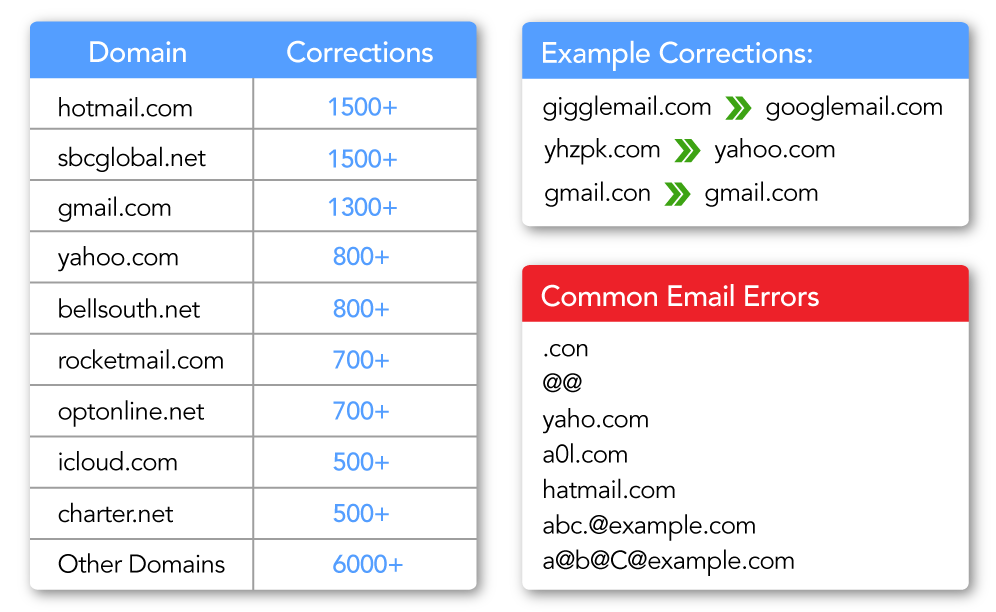
Syntax Checking and Domain Correction
Utilises state-of-the-art fuzzy matching and data correlation algorithms to automatically correct common email errors, such as misspelled domains, outdated providers, and syntax mistakes.
Global Email will validate the corrected and standardised version of the input email. By identifying and fixing typos like “gamail.com” to “gmail.com” prior to validation, the system ensures that each email address is accurate before it’s verified, leading to better results and enhanced mailing lists.
- General Syntax Checking - Enforces universally accepted email syntax rules and standardises the email address.
- Domain Corrections - Corrects the most common misspelling and typos for popular domain names.
- Domain Changes - Corrects outdated domain names belonging to an organisation to their new domain name.
Potentially Harmful Mailbox Types
- Spamtrap Detection - Detects spamtrap addresses at both the mailbox and domain level so you can get ahead of them and safeguard your sender reputation.
- Protected Mailbox Detection - Detects whether the mail provider is notorious for quickly marking unsolicited messages as a spam email.
- Suspicious Character Detection - Identifies characters that are not typically found in email addresses. These types of addresses can be used for advanced attacks, like SQL injection, on a business's infrastructure.
- Identifies Breached Emails - Identifies if, and how many times, an email address has been involved in a data breach in the past.
- Mobile Email Detection - Identifies mobile emails that are protected by FCC regulations. Sending unsolicited emails to these addresses can incur heavy fines.

Negative Indicators
- Disposable Domain Detection - Detects disposable email domains so you can avoid sending messages to temporary emails. Disposables are designed to become inactive after a short period.
- Accept-All Server - Identify mailboxes that are part of an accept-all mail server. These mail servers can claim validity regardless of the true status of an email address.
- Role Address Detection - Detects role addresses, like support@ticketmaster.com, that are unlikely to engage with emails unrelated to their specific function.
- Privacy Flag - Identifies email addresses that may be subject to privacy laws such as GDPR or CCPA.

Malicious Domain Identification
To help protect users and raise threat-awareness, our service continuously monitors trusted industry blacklists to identify domains associated with malicious activity. Flagged domains will fall into one or more of the following four categories; each activity type is returned as a specific result code.
- Phishing Domain - The most common form of email-based cyberattack. Emails from these domains are typically part of attempts to trick users into revealing personal or sensitive information.
- Scam Domain - These domains have been associated with fraudulent schemes, often aiming to deceive or extort recipients.
- Malware Domain - Emails from these domains may carry harmful content intended to inject viruses, spyware, ransomware, or other malicious software onto your devices.
- Malicious Domain - A general flag indicating the domain is tied to one or more types of harmful activity.

Domain Information
- Domain Authentication Methods - Identifies how mail servers authenticate senders, allowing you to meet requirements and ensure delivery.
- Domain Information - Distinguishes between business and personal domains and provides comprehensive insights such as the domain’s locality, administrative organization, and even proxy usage. This helps you better categorise and characterise recipients.
Privacy Flag
The top level domains or countries that may be sensitive to privacy laws. Returns Y for yes and N for no. Handle emails with a Y in privacy flag with caution.
The Privacy Flag will show a “Y” if the Top Level Domain might adhere to privacy laws such as GDPR. For example, the Top Level Domain “.de” is a German Top Level domain. Any Top Level Domain that end with a “.de” will have a “Y” in the Privacy Flag field. Any Top Level Domain that does not adhere to privacy laws will have an “N.”
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of an email verification tool?
An email verification tool checks and validates an email address at the point of entry or in batch to ensure an email address exists and can receive mail. This is important to avoid high bounce rates, being marked as SPAM, increasing deliverability, and protecting your sender’s reputation.
What can an email verification and checking tool be used for?
A global email verification and checking tool validates your email address information and will allow websites and custom applications to update email addresses in your database while verifying and correcting misspelled domain names.
You can use an email verification tool to:
- Verify and correct syntax errors in an address, check for illegal characters and extra “@” characters.
- Verify and correct top-level domain names.
- Check for and correct misspelled domain names.
- Check for and correct domains that have changed.
- Standardise casing in email addresses.
- Perform real-time mailbox validation.
- Check sender blacklist cautions.
- Pace email delivery based on confidence scores.
- Verify the email account (the inbox) does not exist at the given domain.
Why is it important to watch your sender reputation?
An email sender reputation is a score that an internet service provider (ISP) assigns to an organisation. The higher the score, the more likely an ISP will deliver emails to the recipient. on the other hand, if a score falls below a certain threshold, the ISP will more likely direct their emails to the recipients’ SPAM folders.
What affects an email sender’s reputation?
There are several factors that organisations should consider when sending out emails to ensure safe ISP filtering:
- The amount of email sent by the organisation.
- How many emails are being successfully delivered if sending in batch (i.e., email campaigns)
- How many emails bounce due to being incorrect, unknown, or other reasons.
- Level of engagement from recipients; this could mean replying, forwarding, clicking links, or deleting emails from an organisation.
- How many recipients unsubscribe from the organisation’s email list.
- How often an organisation may hit a recipient’s spam trap.
- An organisation’s inclusion on other blacklists.
How to avoid spam traps
Spam traps are a common challenge in email marketing and for organisations trying to outreach. Someone on your contact list changing jobs (and email addresses), subscribers opting out, and even purchased email lists containing bad emails are just a few examples.
Verifying your email list is a straightforward solution to ensure emails are valid and deliverable and flagged for any privacy laws like GDPR.
What is a valid email address?
A valid email address is an address that conforms to the standard format and rules for email addresses. Here are the key components and criteria for a valid email address:
- Local Part: The local part appears before the @ symbol and can contain alphanumeric characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9), as well as certain special characters. Common special characters include period (.), underscore (_), hyphen (-), and plus (+). The local part should not begin or end with a period and should not contain consecutive periods.
- @ Symbol: The @ symbol separates the local part from the domain part in an email address.
- Domain Part: The domain part appears after the @ symbol and typically consists of a domain name and a top-level domain (TLD). The domain name should consist of alphanumeric characters, hyphens, or periods. The TLD can be a generic TLD (e.g., .com, .org, .net) or a country code TLD (e.g., .us, .uk, .au).
- Length Limitations: Email addresses have certain length limitations. The total length of the local part and domain part combined should not exceed 254 characters. However, some email providers may have specific limitations on the length of the local or domain parts.
How do I check if an email is valid?
To check if an email address is valid, you can follow these steps:
- Syntax Verification: Start by checking the syntax of the email address. Ensure it follows basic email formatting, which consists of a local part (before the @ symbol), followed by the @ symbol, and a domain part (after the @ symbol). Additionally, check for common errors like missing or extra characters, spaces, or incorrect symbols.
- DNS MX Record Lookup: Perform a DNS (Domain Name System) MX record lookup for the domain part of the email address. MX records specify the mail servers responsible for handling emails for a particular domain. If there are no MX records found, it suggests that the domain is not configured to receive emails.
- SMTP Verification: Connect to the mail server associated with the email address and initiate an SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) conversation. Start by sending a "HELO" or "EHLO" command to establish the connection. Then, verify the existence of the email address by sending a test email or using the "VRFY" or "RCPT TO" command.
- Response Analysis: Analyse the response received from the mail server. If the server responds with an OK status code (such as 250), it indicates that the email address is valid. However, if the server responds with an error code (such as 550 or 554), it suggests that the email address is invalid or does not exist.
- Disposable Email Address (DEA) Check: Consider checking if the email address is from a disposable email service. Disposable email addresses are temporary and often used for spam or fraudulent activities. Several online services provide databases of known disposable email providers that can be used for this purpose.
- Role Account Check: Some email addresses are not associated with individuals but rather with specific roles or functions (e.g., admin@, support@, info@). While these addresses may be valid, they are not typically used for personal communication.
How often should I perform email verification?
The frequency of performing email verification depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Here are a few factors to consider when deciding how often to perform email verification:
- Email Acquisition Method: If you collect email addresses through an online form or registration process, it's beneficial to validate them in real-time or immediately after submission. This ensures that you capture valid email addresses from the start and prevent the accumulation of invalid or fake addresses in your database.
- Data Age and Source: If you have an existing email database that has been collected over a period of time, some email addresses may become outdated or invalid. In such cases, it's recommended to perform periodic email verification to ensure the accuracy and quality of your data. The frequency can depend on the rate of email address churn in your specific industry or target audience.
- Email Sending Frequency: If you regularly send emails, it's advisable to conduct regular email verification to maintain a clean and deliverable email list. By identifying and removing invalid or inactive email addresses, you improve your email deliverability rates and reduce the risk of being flagged as spam.
- Bounce Rates and Complaints: If you notice an increase in bounce rates (undeliverable emails) or recipient complaints, it may indicate that your email list needs verification. High bounce rates can negatively impact your sender reputation and deliverability. In such cases, you should consider verifying the email addresses in your list promptly.
- System Integration: If you have an automated system or process in place that relies on email addresses, consider incorporating email verification into your workflows. For example, you can verify email addresses during user registration or before sending important communications.
- Budget and Resources: The frequency of email verification may also depend on your available resources and budget. Some email verification services charge based on the number of email verifications performed, so you may need to consider the costs involved.
In general, performing email verification at regular intervals, such as quarterly or biannually, is a good practice to maintain good data quality and deliverability. However, if your email list is rapidly growing or if you have higher email engagement rates, more frequent verification, such as monthly or even weekly, may be beneficial.
What are disposable emails?
Disposable emails, also known as temporary or throwaway emails, are email addresses that are created for short-term use or for a specific purpose. They are often used to protect personal information and maintain privacy when signing up for online services, accessing gated content, or participating in forums or discussions.
Some benefits of disposable emails include:
- Temporary Nature
- Anonymity and Privacy
- Email Forwarding or Self-Destruction
- Quick Setup
- Anti-Spam Measures
- Limited Functionality
- Publicly Available
It's important to note that while disposable email addresses provide convenience and privacy, they can also be misused for fraudulent activities, spamming, or creating fake accounts. To mitigate these risks, some online platforms and services implement measures to detect and block disposable email addresses during registration or communication processes.
Achieve Complete Contact Data Management
Melissa's Data Quality tools help organisations of all sizes verify and maintain data so they can effectively communicate with their customers via postal mail, email, and phone. Our additional data quality tools include
Address Verification
Phone Verification
Name Verification
Data Deduplication
Ready to Start Your Demo?
Start today with Melissa's wide range of Data Quality Solutions, Tools, and Support.






